Binary Bomb Phase 6 Walkthrough
I completed the course ‘Architecture 1001: x86-64 Assembly’ from Open Security Training 2, and there was a very nice challenge in this course - Binary Bomb.
You can find the challenge binary here - https://gitlab.com/opensecuritytraining/arch1001_x86-64_asm_code_for_class/-/tree/master/binary_bomb_lab/windows?ref_type=heads
I will be walking through the last phase - 6 of the Binary Bomb challenge using WinDbg.
Open the executable with the solutions file path in the argument. The solutions file would be containing the solutions to previous 5 phases in separate lines.
Reload the symbols -> .reload /f
Disassemble the phase_6 function -> uf phase_6
Below is the C code written after analysing the assembly instructions:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int value;
int index;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node* createNode(int val, int index) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->value = val;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
int phase6(int inp[])
{
struct Node* ll1 = createNode(0x212,1);
struct Node* ll2 = createNode(0x1c2,2);
struct Node* ll3 = createNode(0x215,3);
struct Node* ll4 = createNode(0x393,4);
struct Node* ll5 = createNode(0x3a7,5);
struct Node* ll6 = createNode(0x200,6);
ll1->next = ll2;
ll2->next = ll3;
ll3->next = ll4;
ll4->next = ll5;
ll5->next = ll6;
struct Node* head = ll1;
//first part
int a = 0;
while(a < 6)
{
if(inp[a] >=1 && inp[a]<=6)
{
int b = a + 1;
while(b < 6)
{
if(inp[a] != inp[b])
{
b++;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
a++;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
printf("first part done!\n");
//second part
a = 0;
struct Node* narr[6] = {0};
struct Node* curr = NULL;
while(a < 6)
{
curr = head;
int b = 1;
while(b < inp[a])
{
curr = curr->next;
b++;
}
narr[a] = curr;
a++;
}
head = narr[0];
curr = head;
//third part
a = 1;
while(a < 6)
{
curr->next = narr[a];
curr = curr->next;
a++;
}
//fourth part
curr->next = NULL;
curr = head;
a = 0;
while(a < 5)
{
if(curr->value < curr->next->value)
{
return(0);
}
else
{
curr = curr->next;
a++;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int inp[] = {5,4,3,1,6,2};
int out = phase6(inp);
if(out == 0)
{
printf("Game over, bomb exploded\n");
}
else
{
printf("Game completed\n");
}
}
Let’s go through the assembly step-by-step and map it to the C code:
- We see a call to the function ‘read_six_numbers’. Add a breakpoint on the call instruction if you want to explore the function.
- The function
read_six_numberswill takercx,rdxas arguments.rdxis set with the address ofrbp+48h. The user input values will be set from the address starting atrdx, and hencerbp+48hwill have the input values.
- Add breakpoint to check the output of read six numbers. It can be seen that even if the input contains more than 6 digits, the output is 6, so it could mean that first 6 digits would be considered.
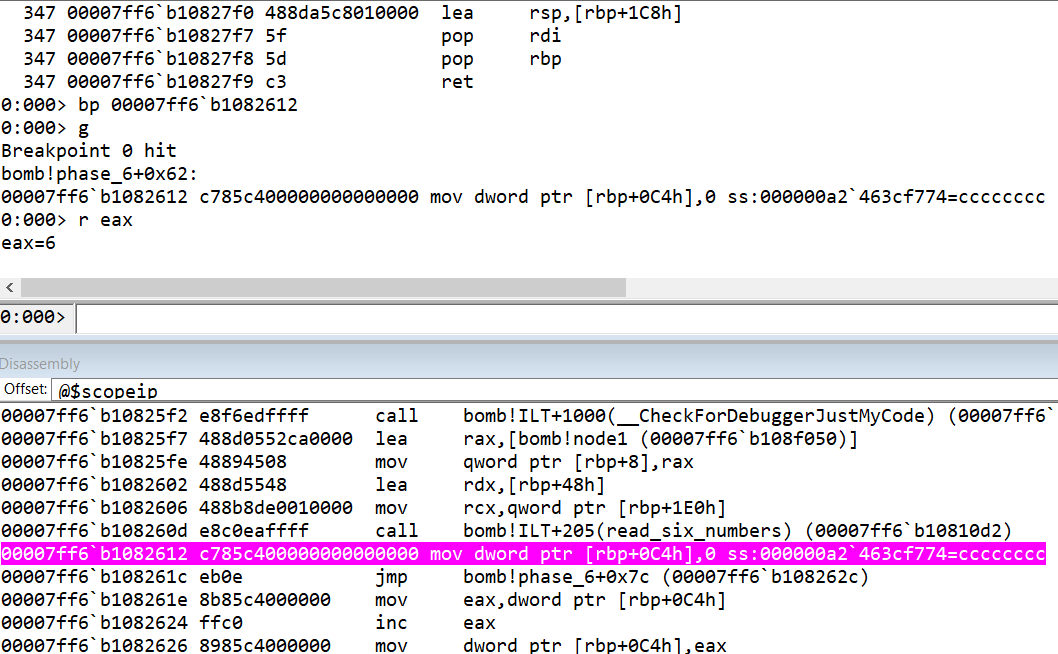
After the call to read_six_numbers, a variable
rbp+0c4h(let’s call this as variablea) is set to 0 and there is jump statement.The jump statement takes the control to the compare function. This function checks if the value of the variable is greater than or equal to 6.
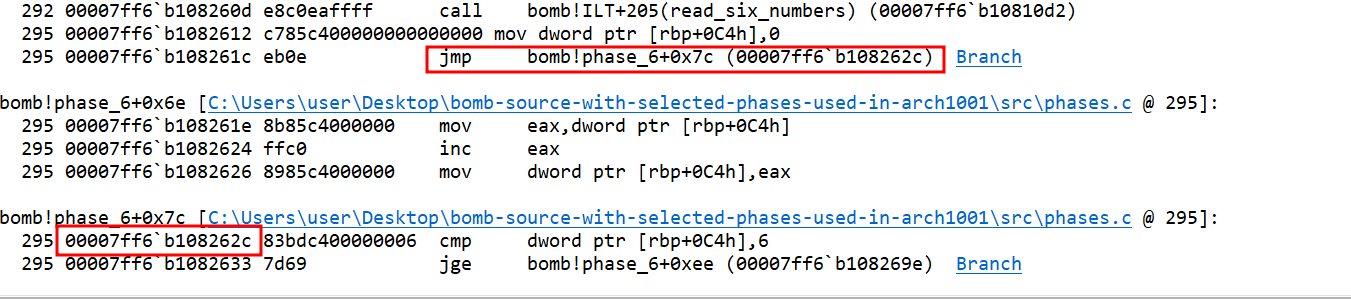
- If the value is greater than equal to 6, the jump statement is executed and takes the control to a different location which is outside the loop. This seems like the false condition for a loop.

- But, if the value of
ais less than 6, the jump does not take place and flow continues after the jump statement.
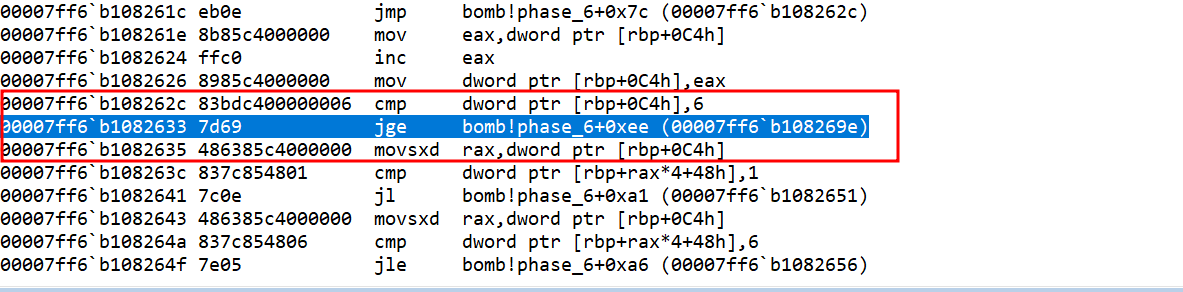
rbp+48hhad the user input values. The value of variableais being used as an array index (let’s call the array asinp). The value of array at index ainp[a]is compared with 1. If the value turns out to be less than 1, the explode_bomb is function being called with jump statement.

- If the value of
inp[a]is more than 1, then again theinp[a]is being compared with 6. If the value is greater than 6, the jump statement is not executed and explode_bomb function will be called. So, the value ofinp[a]should be in range of 1 and 6.
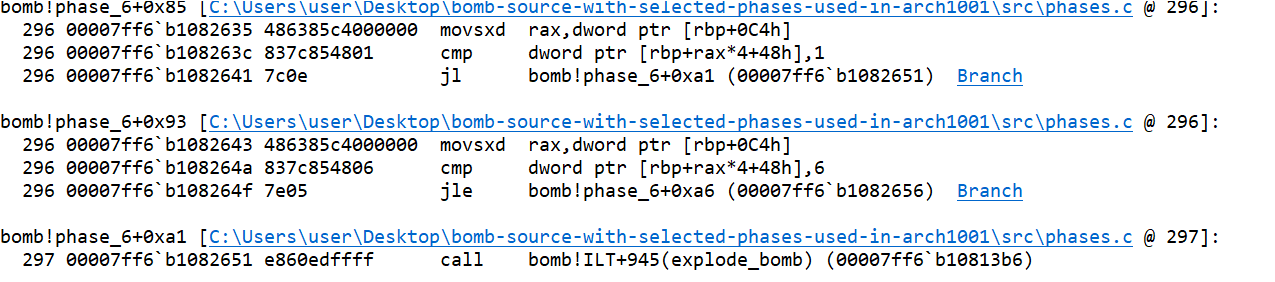
- If the value of
inp[a]is less than or equal to 6, then a new variablerbp+0e4h(let’s call it variableb) is assigned the valuea+1.

- The jump statement takes the control to a condition statement, where the value of
bis compared with 6.

- If the value is greater than or equal to 6, the jump statment again takes control to the increment operation of variable
a.

- If the value of
bis less than 6, then there is a comparison betweeninp[a]andinp[b].

- If the values are equal, the jump statement is not taken, and explode_bomb function is called. If the values are not equal, the jump statement takes the control to increment of variable
band back to the loop condition of comparison of valuebwith 6.
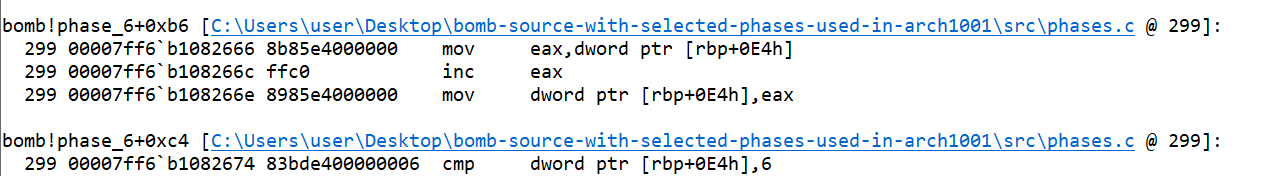
- Now, if we go back and look around the read_six_numbers function, there is an instruction related to node. Address of this node is saved to
rbp+8.

- If we try to print the value at address, we could see that it contains a different address as well. We can print that too, and find a pattern.

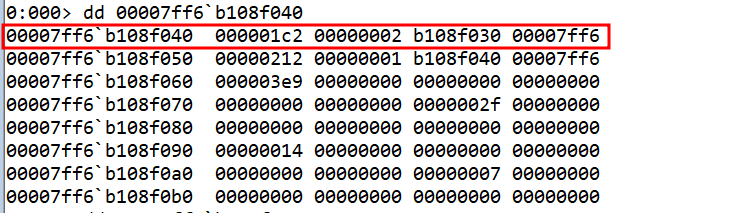
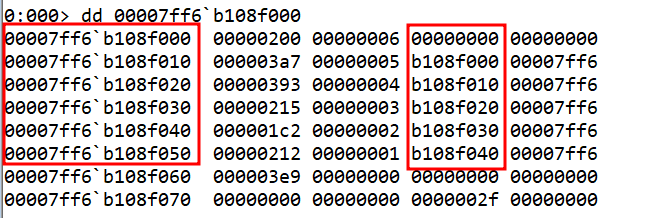
This shows a Linked List structure where each node has a value and reference the next node address. The last node with the address b108f000 seems to be the last node, as it doesn’t point to another address.
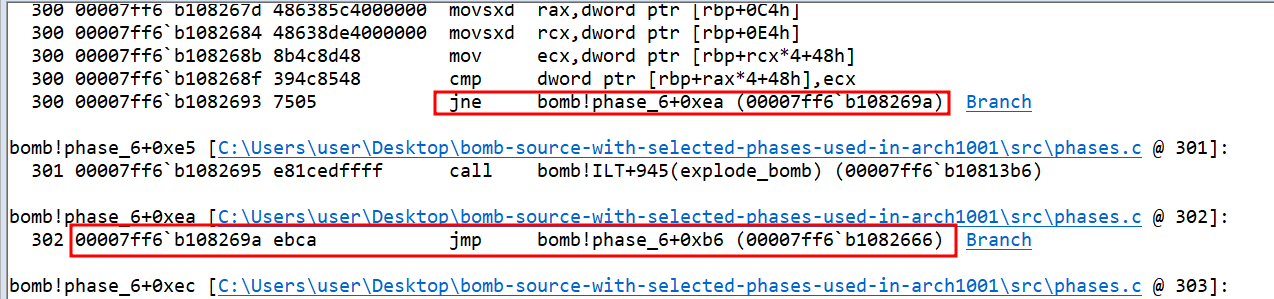
When the condition of main loop became false, the just statement took the control to outside the loop where the value of
ais set to 0 and then jump statement takes to another condition whereais compared with 6. This seems to be the start of another main loop.

If the value of
aagain is greater than or equal to 6, the control passes to a different location.If the value of
ais less than 6,rbp+8which contains the address of first linked list node, is passed torbp+28h. The value ofbis set to 1. Let’s call the node atrbp+8ashead, andrbp+28hascurr(current).

- The value of
bis compared with the value of array at indexa. If value ofbis less, the value ofcurris set tocurr->next(the next node). For each node, the value at the address is the node value, then there is index, and then the address to next node. So, the+ 8, gives the address of next node.
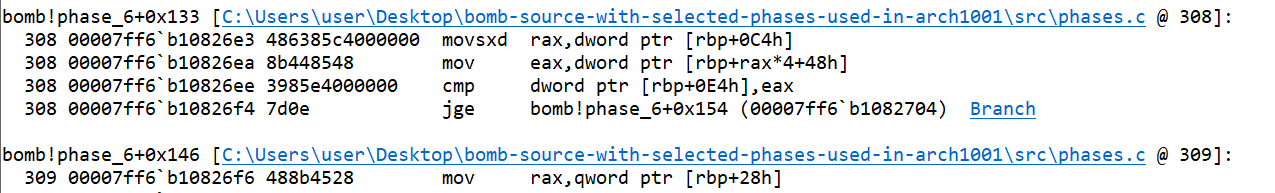
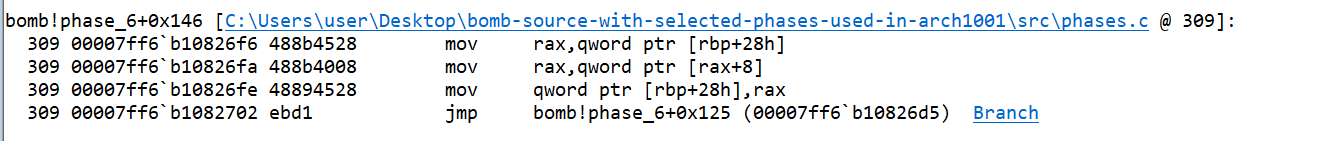
- The value of
bis increased by 1 and agin the comparison starts, so it means the comparison ofbwith value of array at indexawas a loop condition (nested loop) and here the loop ends.

- If the value of
bwhen compared with value of array atawas greater, then the jump would pass the control outside the inner loop.rbp+78hcontained the address of the start of the node of linked list. From this address, an array is taken (let’s call itnarr), whose value at index anarr[a]is set with the value ofcurrnode.

- Jump instruction takes the control to iteration where the value of
ais incremented by 1, and again the condition is checked, which means the loop ends.
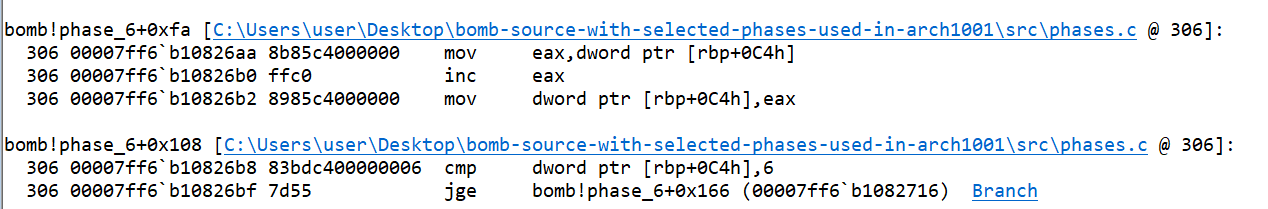
- If the value of
abecomes greater than or equal to 6, then the loop condition breaks and control passes outside the loop. The address atrbp+78h(narr[0]node array) is being set torbp+8(headnode). The address fromrbp+8(head) is being set torbp+28h(currnode).
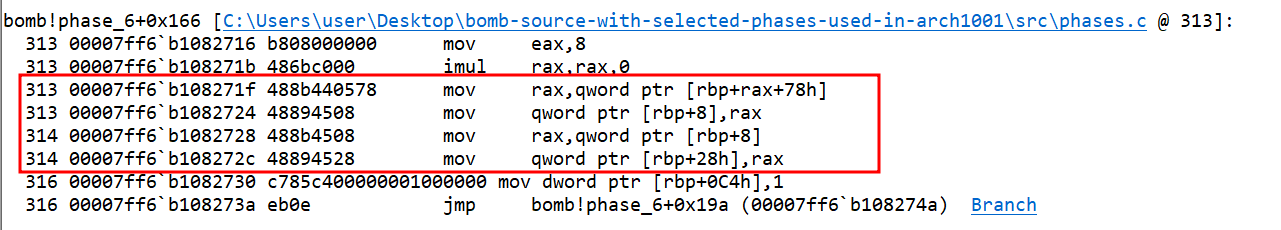
- We can check the value of
rbp+78(narr) has address of different nodes of the linked list.
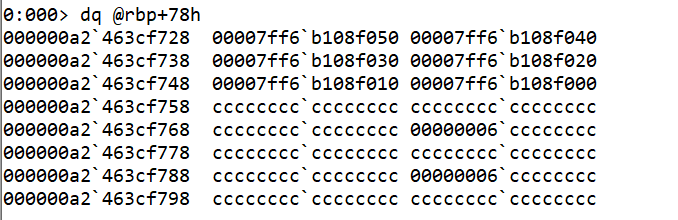
- We can break at the line where
rbp+28h(curr)is assigned and check the value. It has the starting node address of linked list.
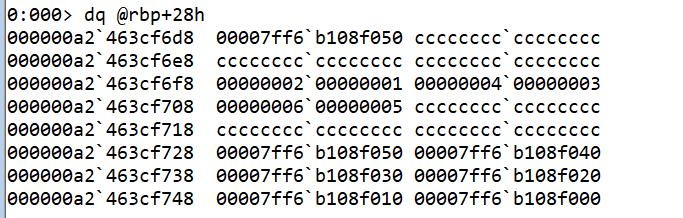
So, this indicates something like
head = narr[0]; curr = head;The value of
ais set to 1, and jump takes the control to a comparison statement which again compares the value ofawith 6. This could be the start of another loop.

If the value of
ais greater than or equal to 6, the jump statement takes the control to a different location.If the value of
ais less, the loop starts/continues. Thecurrnode (rbp+28h) next element is set to the node at indexaof the node arraynarr(curr->next = narr[a]). Thencurrnode is again set tocurr->next.
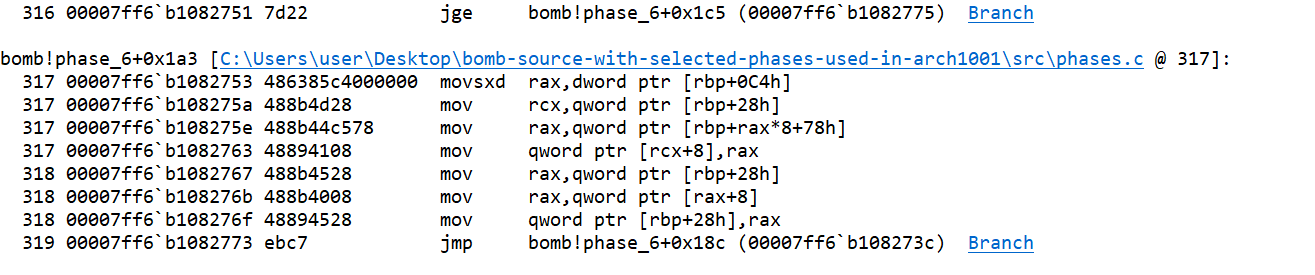
- The jump instruction takes the control to iteration where the value of
ais increased by 1. After the iteration again there is the comparison statement ofawhich is the loop condition, so the loop ends.

- If the value of
abecomes more than or equal to 6, the loop breaks and control moves out of loop. Thecurrnode next address is set to 0, which indicates to NULL. It means that thecurrnode does not point to any other node. - Then the
currnode is pointed to theheadnode. Value ofais set to 0.
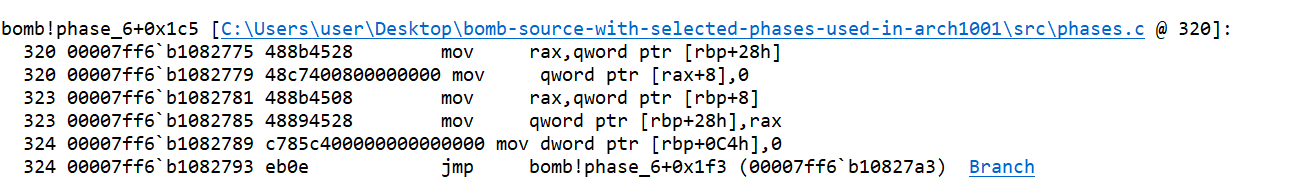
- The jump statement then takes the control to the comparison instruction. If the value of
ais greater than or equal to 5, jump statement takes the control to another location.

- If the value of
ais less than 5, comparison happens between values ofcurrandcurr->next. Ifcurrvalue is less thancurr->nextvalue, theexplode_bombfunction is being called.
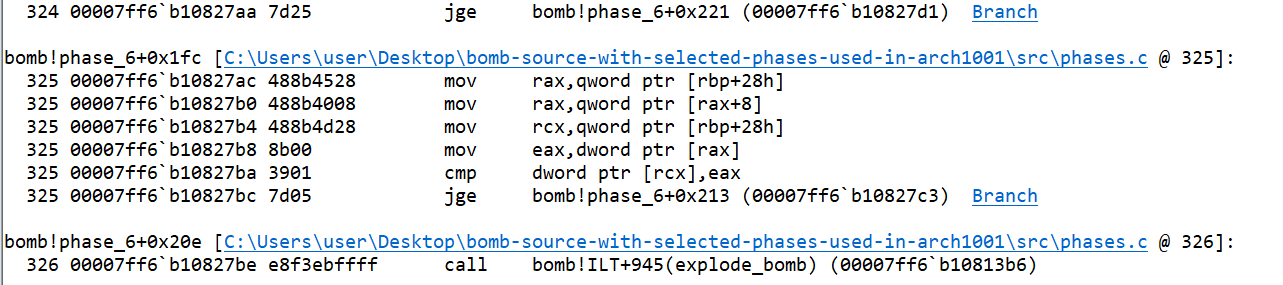
- If the value of
curris equal to or greater than value ofcurr->next, thencurrnode is set tocurr->nextnode.

- The jump statement takes the control to iteration where the value of
ais increased by 1. The loop condition comes again, which means that the loop ends.

- If the value of
ais greater than or equal to 5, the control passes outside the loop.
The program ends here.
To create the C program, we need to create the nodes of the linked list. We can take the values of nodes as shown in the assembly code by printing the values at 00007ff6`b108f000.
- The first loop is trying to check if the user input values are also distinct.
- The second loop is trying to put different nodes at different array index based on an algorithm. Our input is used to set the order of nodes in the array.
- The third loop is trying to make links between different nodes of the array to form the linked list.
- The fourth loop is trying to check if the nodes of linked list are linked in the descending order of their values.
So, we should input the numbers such that the nodes at those indices (our inputs) be in descending order of their value.